Legal Notice For Cheque Bounce

Date : 13 Mar, 2024
Post By admin
Written By : Advocate Hitesh Katharotiya | 18 years of experience | ★★★★★
In the realm of financial transactions, the repercussions of a cheque bounce can unsettle the smooth course of business dealings, prompting the need for a precise and legally sound response. The issuance of a legal notice drafting in such instances not only signifies a formal redressal approach but also serves as a pivotal juncture in the resolution process. As we embark on unraveling the intricacies surrounding the formulation of a comprehensive legal notice for a cheque bounce, we will uncover essential strategies and considerations that can potentially alter the trajectory of such disputes. Stay tuned to explore the critical elements that underpin this legal recourse and how it can shape the outcome of a cheque bounce scenario.
Legal Framework Overview
The legal framework pertaining to the process of drafting a legal notice for cheque bounce is a critical aspect that must be meticulously understood and adhered to in order to ensure the effectiveness and legality of the notice. Under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, a legal notice is a prerequisite before initiating a case against the drawer of the bounced cheque.
Key Elements of the Legal Notice:
-
Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act: The legal notice is mandated by Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, as a precursor to legal action for a bounced cheque.
-
Inclusion of Details: The notice should include specific details such as the amount involved, the reason for non-payment, and a demand for payment to be made within a specified time frame, usually 15 days.
-
Formal Communication: The legal notice serves as a formal communication to the drawer, notifying them of the dishonored cheque and providing an opportunity to settle the issue without involving legal proceedings.
-
Opportunity for Settlement: It offers the drawer an opportunity to rectify the matter by making the payment within the stipulated time frame mentioned in the notice.
-
Initiating Legal Action: Failure to respond to the legal notice within the stipulated time can result in the initiation of legal action, including filing a case in court for the recovery of the amount due along with legal costs.
By adhering to the legal procedures diligently and ensuring the inclusion of essential details, the payee can protect their rights and facilitate a swift resolution to the cheque bounce case. Understanding the legal framework is crucial for drafting an effective legal notice in accordance with the requirements of the Negotiable Instruments Act.
Cheque Bounce Consequences
Having properly served the legal notice in compliance with the provisions of the Negotiable Instruments Act, the consequences of a cheque bounce can significantly impact both parties involved in the transaction. When a cheque bounces, several repercussions may follow:
- Financial Loss: The payee may face financial difficulties due to the cheque bounce, especially if they were relying on the funds for a specific purpose.
- Legal Action: The payee has the right to take legal action against the drawer of the bounced cheque. This can involve filing a complaint in court within 30 days from the date of receiving the memo from the bank about the cheque bounce.
- Liability: The drawer of the bounced cheque may be held liable to pay the cheque amount along with additional penalties as per the law, which can tarnish their financial reputation.
Issuing Legal Notice
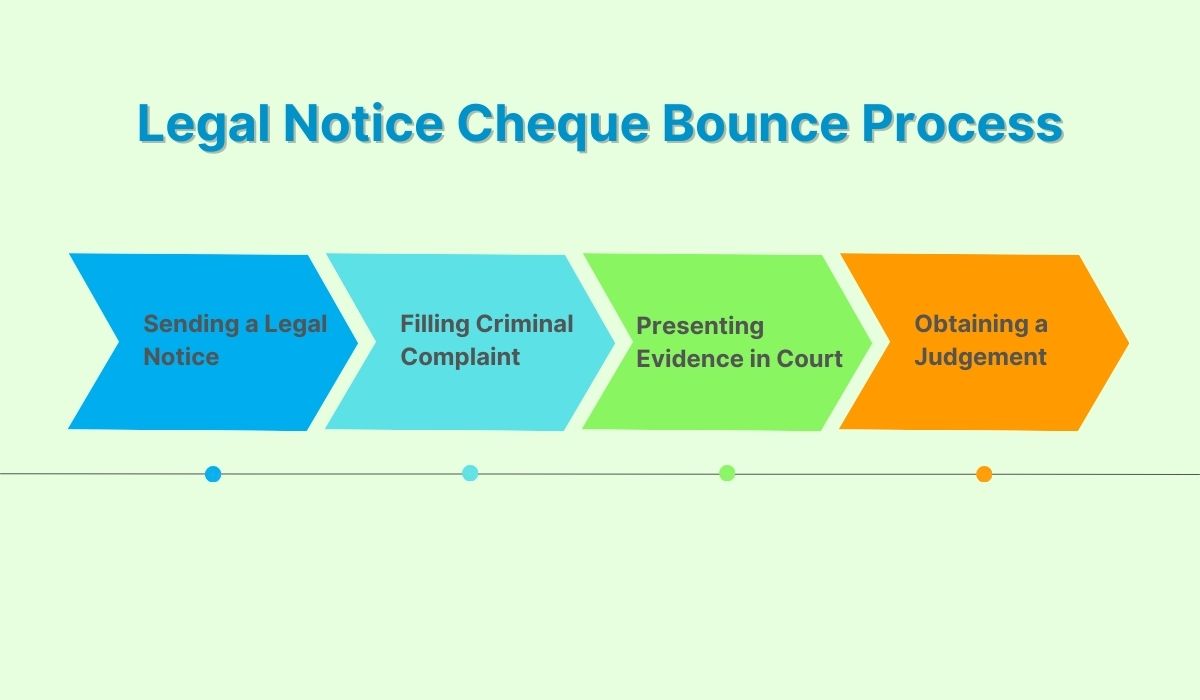
Upon the occurrence of a cheque bounce, the essential step towards resolving the matter is the issuance of a legally compliant notice to the defaulter. A legal notice for a cheque bounce serves as a formal communication alerting the defaulter about the dishonored cheque due to insufficient funds or other reasons stated in the return memo from the bank. This notice typically outlines the details of the cheque bounce, demands the payment of the due amount within a specified notice period, and warns of potential legal action if the issue is not resolved promptly. Failure to respond to the cheque bounce notice can lead to the initiation of a cheque bounce case, which is considered a criminal offence in many jurisdictions. Subsequently, the aggrieved party may proceed with filing a criminal complaint against the defaulter, escalating the matter further. Therefore, issuing a cheque bounce notice is crucial in initiating the resolution process and avoiding prolonged legal disputes.
Key Information Required
After issuing the legal notice for cheque bounce, gathering key information required plays a crucial role in preparing a comprehensive and effective notice. To ensure the legal notice is well-drafted and serves its purpose, the following information is essential:
- Client Details: Collect accurate information about the client involved in the cheque bounce case, including their full name, address, contact details, and any relevant identification numbers.
- Cheque Details: Obtain specifics regarding the bounced cheque, such as the cheque number, date, amount, and the reason for dishonor as provided in the cheque return memo.
- Agreement Terms: Refer to the agreement or contract under which the cheque was issued, highlighting relevant clauses pertaining to cheque bounce consequences and legal actions.
Ensuring these key details are gathered and included in the legal notice will strengthen the case and pave the way for further legal proceedings in India related to the dishonoured cheque, in accordance with the laws governing banking institutions.
Timelines and Deadlines
Promptly adhering to the prescribed timelines and deadlines is crucial in the process of handling a cheque bounce case within the legal framework. When a cheque is dishonored by a financial institution, the first step is to issue a legal notice to the defaulter. This legal notice must be sent within 30 days of receiving the memo from the bank about the bounced cheque. The defaulter then has 15 days from the receipt of the legal notice to settle the dues. If the payment is not made within this period, the next course of action is to engage a lawyer to file a civil suit in the appropriate jurisdiction, typically the district court. It is essential to ensure that all necessary documentation, including proof of the bounced cheque, legal notice, and communication with the defaulter, is in order and submitted within the specified timelines. Failure to adhere to these deadlines could result in delays or complications in the legal proceedings.
Legal Notice Format
To draft a legally effective notice for a bounced cheque, meticulous attention to detail in the format is imperative. The legal notice format is crucial in cheque bounce cases as it sets the tone for further legal proceedings. Here are essential elements to consider when drafting a legal notice for a cheque bounce:
- Clear Identification: Clearly identify the parties involved, including the sender of the notice, the recipient, and any other relevant parties.
- Statement of Facts: Provide a detailed account of the cheque bounce incident, including the date of issuance, the amount, and the reason for the bounce, such as insufficient funds.
- Legal Consequences: Clearly outline the legal consequences if the matter is not resolved promptly, such as initiating a summary suit or a criminal case.
Ensuring that the legal notice format adheres to the law and includes all necessary details is crucial for a successful resolution in cheque bounce cases.
Serving the Notice
Upon the occurrence of a cheque bounce incident, the next critical step involves serving the legal notice to the defaulter. When a cheque is dishonored due to non-sufficient funds in the account, the payee can proceed by sending a legal notice to the drawer of the bounced cheque. This notice serves as a formal communication highlighting the dishonored cheque and demanding the payment of the due amount, including any cheque bounce charges as per the Negotiable Instrument Act.
The legal notice should clearly state the details of the bounced cheque, the amount owed, any additional charges incurred, and a reasonable period for the defaulter to settle the dues. It is essential to ensure that the notice is drafted accurately, mentioning the consequences of non-compliance, such as legal action or prosecution. The notice should be sent through registered post or delivered personally to ensure acknowledgment of receipt. Serving the notice is a crucial step towards resolving the cheque bounce issue before escalating it further, potentially leading to court proceedings and bail amounts being set.
Next Steps After Notice
What should be the immediate course of action following the legal notice for cheque bounce? Once the legal notice for a bounced cheque has been served, it is crucial to proceed with the appropriate steps to address the situation effectively. Here are the next steps that should be considered:
- Review Legal Options: Seek legal advice to understand the implications of the notice and determine the best course of action to resolve the cheque bounce issue.
- Communicate with the Issuer: Open a line of communication with the issuer of the bounced cheque to discuss possible resolutions and avoid escalating the matter further.
- Prepare for Legal Action: If necessary, start preparing for potential legal proceedings by gathering relevant documents and information to support your case in the event that legal action is pursued.
Out-of-Court Settlement Options
Consider exploring potential out-of-court settlement options to resolve the cheque bounce issue amicably and efficiently. An out-of-court settlement can be a beneficial way to avoid prolonged legal proceedings and maintain a positive relationship between the parties involved in the cheque bounce incident.
Key Considerations for Out-of-Court Settlement:
-
Mutually Agreeable Solution: Both parties can negotiate terms that suit their interests and reach a mutually agreeable solution.
-
Time and Cost Savings: This approach can save time, costs, and the stress associated with a formal court case.
-
Clear Documentation: Ensure that all discussions and agreements are documented clearly, including details such as the agreed-upon resolution, payment terms, timelines, and any other relevant conditions.
-
Record-Keeping: Keep records of all communication and transactions related to the settlement to avoid potential disputes in the future.
-
Preserving Reputation: Engaging in an out-of-court settlement can help preserve the reputation of both parties involved, especially in cases where the cheque bounce incident is linked to business or financial matters.
By proactively seeking a resolution outside of court, both parties can demonstrate professionalism and a willingness to address the issue promptly and effectively.
Seeking Legal Recourse
Embarking on the path of legal recourse is often a strategic step taken in response to a cheque bounce incident, signaling the initiation of formal legal proceedings. When seeking legal recourse for a cheque bounce, certain key steps need to be followed to navigate the complex legal landscape effectively:
- Issuance of Legal Notice: The first step in seeking legal recourse for a cheque bounce is sending a legal notice to the defaulter, informing them of the bounced cheque and demanding payment within a specified period.
- Filing a Suit: If the defaulter fails to comply with the legal notice, the next course of action is to file a suit in the appropriate judicial district. This formal legal action aims to recover the amount mentioned in the bounced cheque along with any applicable penalties.
- Understanding the Offence: It is essential to comprehend the legal implications of cheque bounce as it is considered a criminal offence under the Negotiable Instruments Act, impacting both the issuer and receiver of cheques.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of drafting a legal notice for a cheque bounce is a crucial step in seeking redress for dishonored payments. Understanding the legal framework, key information requirements, timelines, and serving procedures is essential for navigating this complex legal procedure effectively. By following the appropriate steps and seeking legal recourse, individuals and businesses can assert their rights and work towards resolving cheque bounce issues in a structured and informed manner.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Can a Legal Notice for Cheque Bounce Be Drafted by an Individual Without the Help of a Lawyer?
Ans. Yes, individuals can draft a legal notice for cheque bounce without a lawyer's assistance. However, it is advisable to seek legal guidance to ensure accuracy and compliance with relevant laws. Legal notice drafting requires precision and understanding of legal language.
Q2. Is There a Specific Format That Must Be Followed When Drafting a Legal Notice for Cheque Bounce?
Ans. Yes, there is a specific format that must be followed when drafting a legal notice for cheque bounce. It should include details like the date, name of the recipient, nature of the default, demand for payment, and consequences of non-compliance.
Q3. What Are the Potential Consequences for Not Responding to a Legal Notice for Cheque Bounce?
Ans. Failure to respond to a legal notice for cheque bounce can lead to legal action, including a lawsuit filed against the defaulter. This may result in court judgments, financial penalties, damage to credit rating, and potential criminal charges.
Q4. How Can One Ensure That the Legal Notice Is Properly Served to the Defaulter?
Ans. Ensuring proper service of a legal notice involves adhering to legal requirements for delivery methods, such as registered mail or process servers. Verification of receipt is crucial to confirm the defaulter has been officially notified as per legal standards.
Q5. What Options Are Available if the Defaulter Does Not Respond to the Legal Notice for Cheque Bounce?
Ans. If the defaulter does not respond to the legal notice for cheque bounce, options include initiating legal proceedings, filing a complaint with the appropriate authority, and pursuing civil remedies. Legal counsel can guide through the process efficiently.





